Various methods have been designed specifically to help a trader limit his losses and protect his investment against risks. In this article, you’ll learn about one of such protection instruments. It is called hedging.
“Hedging” is a means of protection, control, or limitation. It’s the activity of reducing the risk of losing money on shares, bonds, etc. Traders use hedging when they have an open trade which can potentially go in a wrong direction and result in losses.

To protect his trades, a trader often uses currency pairs correlation. “What does it even mean, pairs correlation?” – you may ask. Correlation is relationship between currency pairs. Instruments can move simultaneously, in the same or in opposite directions. Some assets have positive correlation, and there are assets with negative correlation. Instruments with positive correlation move in the same direction, in tandem. In case of negative correlation, currency pairs trade in opposing directions simultaneously.
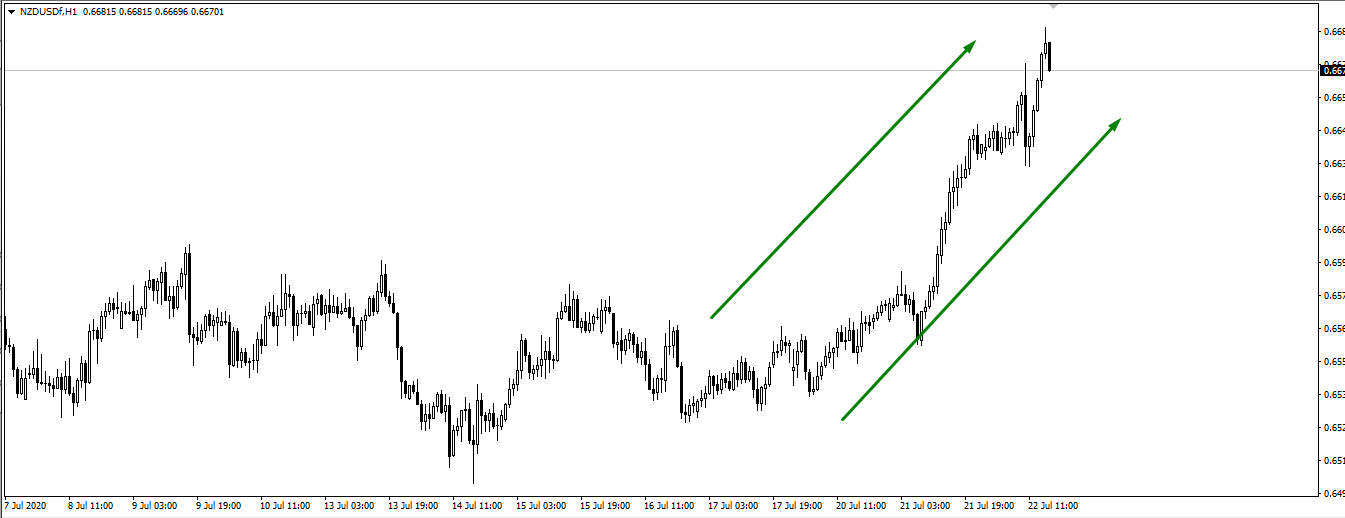
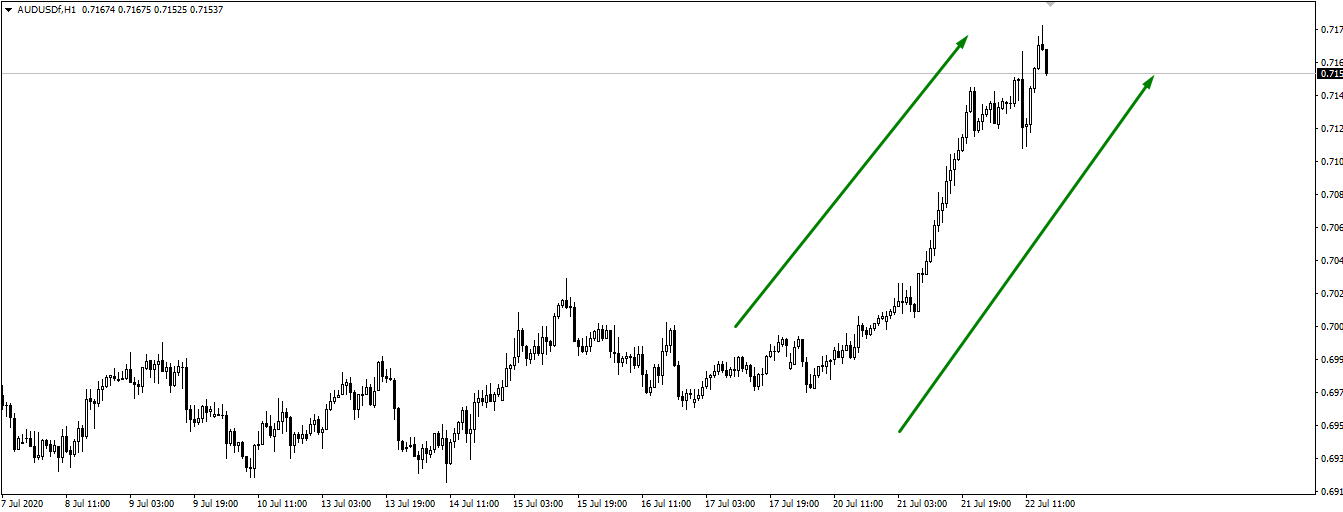
Good examples of currency pairs with positive correlation are NZD/USD and AUD/USD. As you can see in the charts, the two pairs are moving in the same direction.
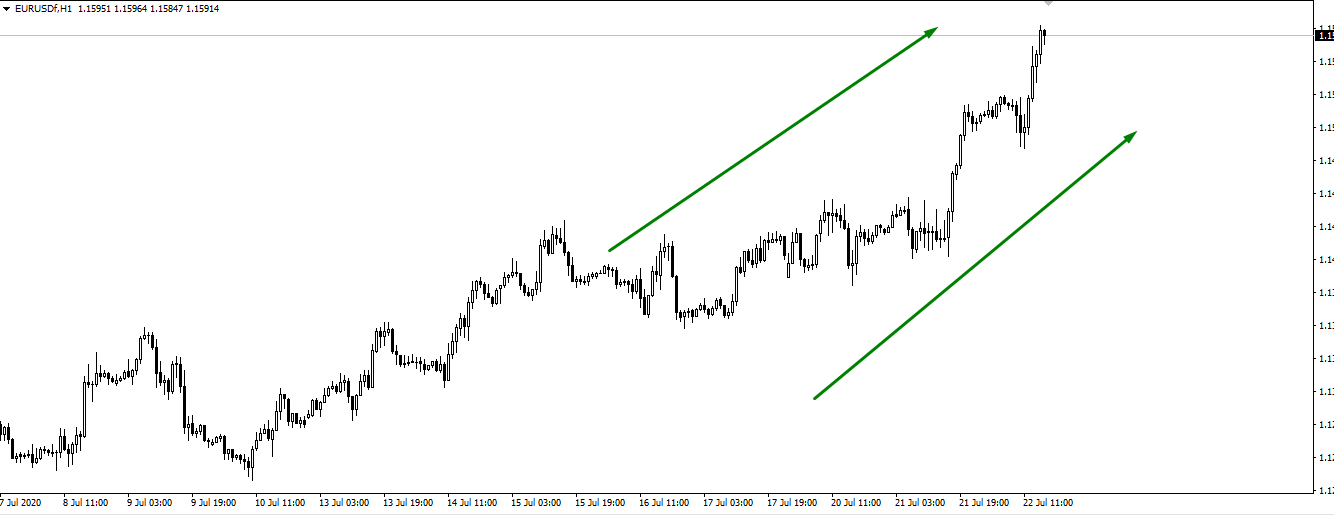
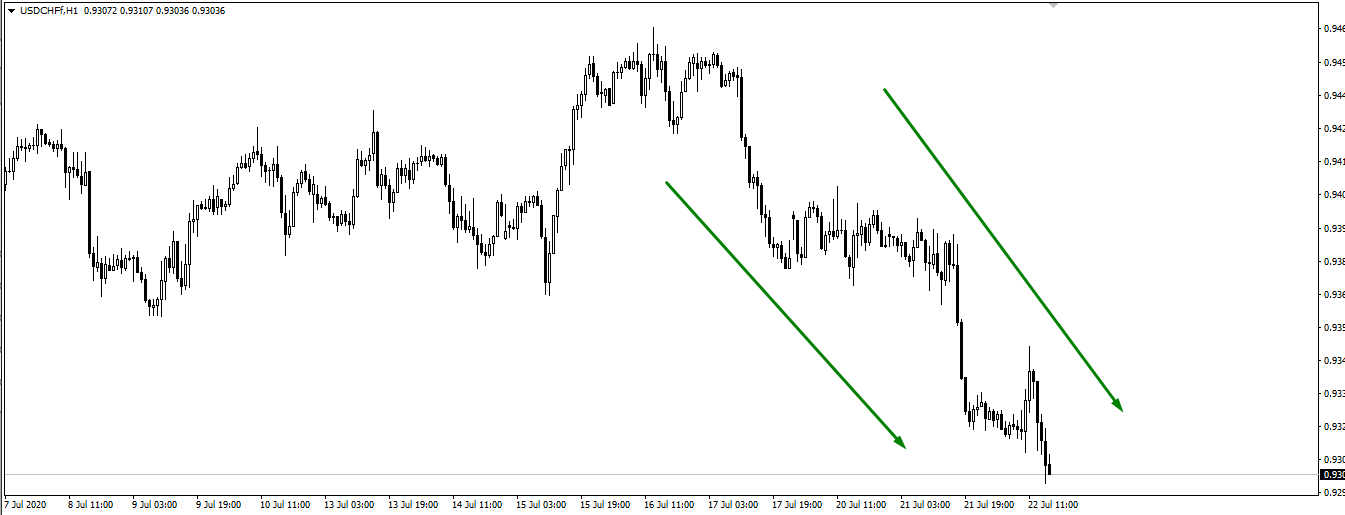
EUR/USD and USD/CHF pairs, on the other hand, are the example of negative correlation, when one asset is moving up, and the other one heads down.
Hedging methods
So, how can you hedge against risks?
- First of all, you can buy instruments that move in opposite directions;
- Second, you can buy and simultaneously sell assets that are closely correlated with each other;
- Also, we can open multi directional trades for one trading instrument at the same price;
- And finally, you can open multi directional trades in the same asset, but at different prices.
The last 2 hedging methods are called “locking“. The “lock” is often set when the market situation has changed dramatically and the trade is in drawdown. If a trader assumes that there is a chance for price to return to the positive territory, he can sit it out in the “lock” and escape the losing trade when the right moment comes. Such approach will at least allow the trader to limit his losses, and maybe even to wait out the storm and return to a surplus.
Types of hedging
- Let’s start with full hedging, which implies trades that completely cover losses. Such transactions are opened with the same volume and value.
- Next, we have partial hedging, which will protect only part of your investment.
- Selective hedging is based on opening trades that differ in volume and time of market entry. With selective hedging, assets should be highly volatile and this method is only suitable for day trading.
- When hedging, you need to strictly follow your trading strategy and risk management rules. Everyone chooses the risks for themselves, but according to general standards, the loss in one transaction should not exceed more than 5% of your deposit. If trading instruments are closely correlated, you should use no more than 10% of your capital.
As you can see, hedging is an extremely complicated technique, and we don’t recommend using it if you have no or little experience. Only a deliberate and well-thought out approach will turn hedging into an effective tool that will protect your investment against losses.
If you like our articles, follow us on Facebook and Instagram. Stay tuned for more interesting posts on our blog. We post new material several times a week.